Energy Ratings vs U-values
Whether it is new-build or replacement windows, it is likely you will have heard about energy ratings and U-values at some point.
You may know that these are important, but you might not know exactly what a U-value is, what is included in an energy rating, or how to choose your doors and windows wisely, based on the ratings you need to achieve.

What is a U-value?
A "U-value" is the measurement of heat transferred from one side of a window (or door) to the other.
You can also call it "thermal transmittance".
The lower the U-value, the less heat that would be lost through the door or window.
A U-value is used to determine the energy efficiency of windows, doors and other building products.
Putting it technically, it is the rate of transfer of heat through a structure, divided by the difference in temperature across that structure (W/m²K).

What is an Energy Rating?
Energy Ratings provide an overall rating of how energy efficient a window or door is, taking into account several different factors including the U-value, air flow, etc.
Window manufacturers can show the energy efficiency of their products using an energy-rating scale from A++ to E. The entire window (the frame and the glass) is assessed to allow for heat loss, draughts and solar gain, giving a rating that indicates the overall impact of fitting that window in your home.
Single, double or triple glazing - the differences
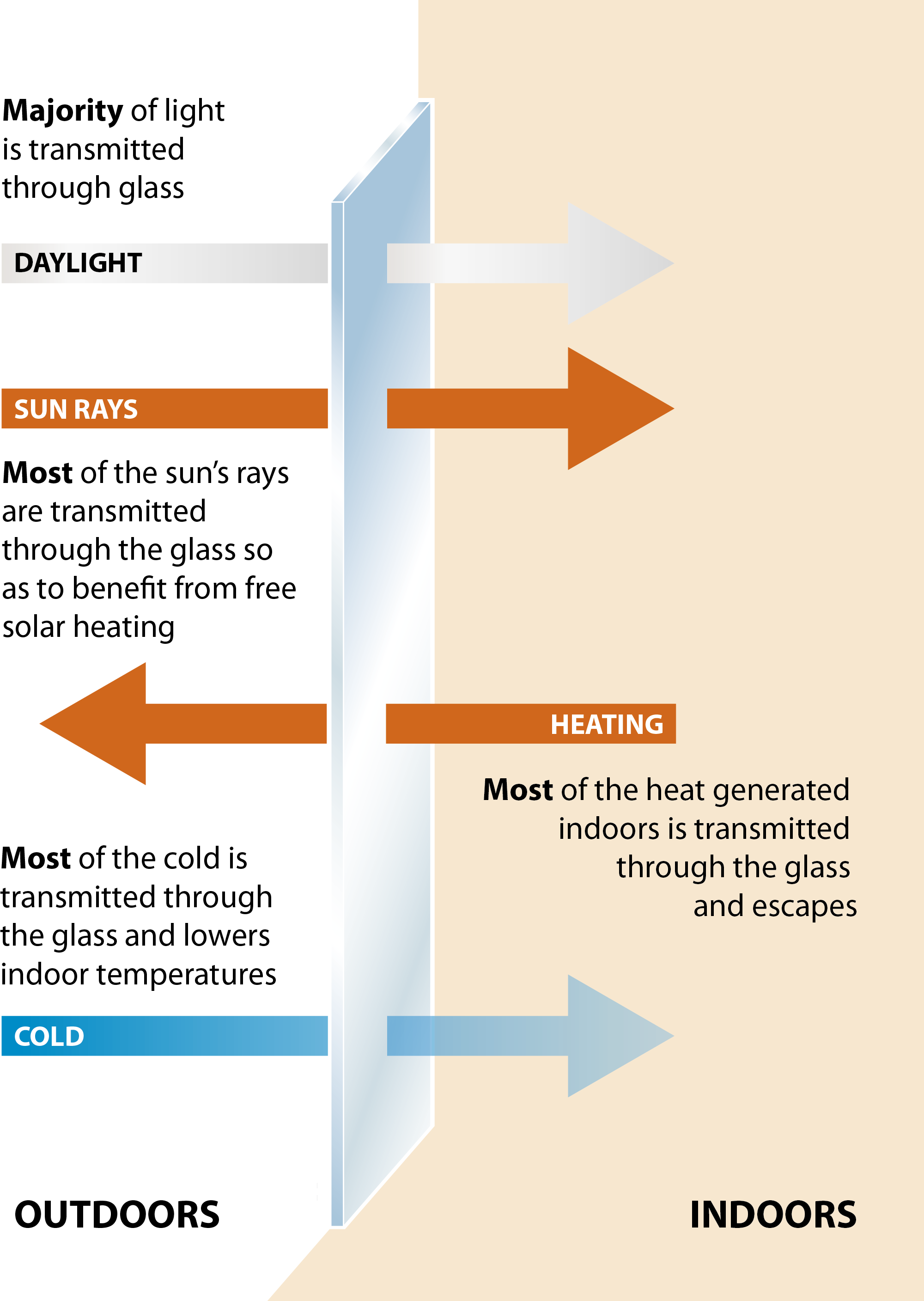
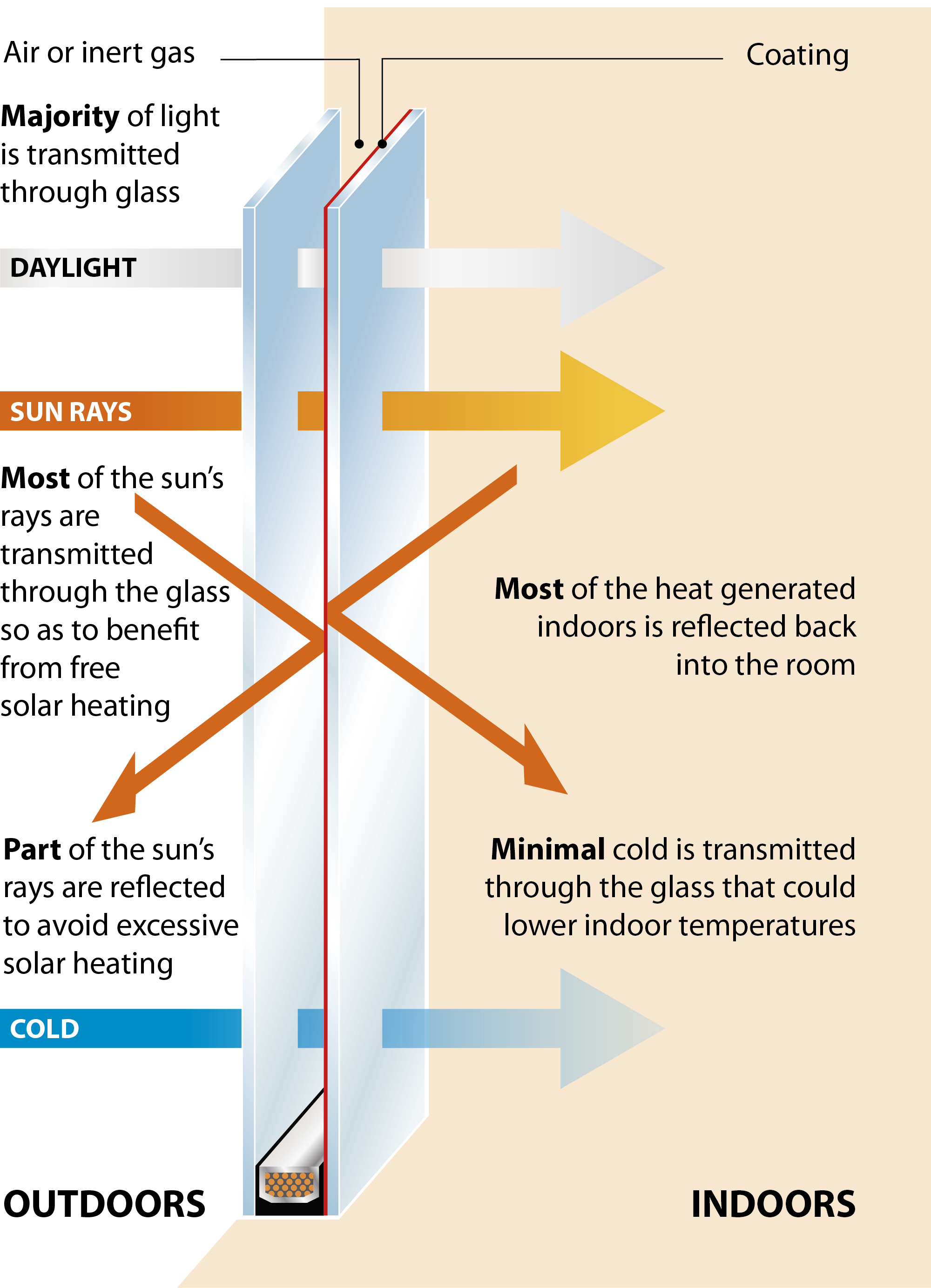
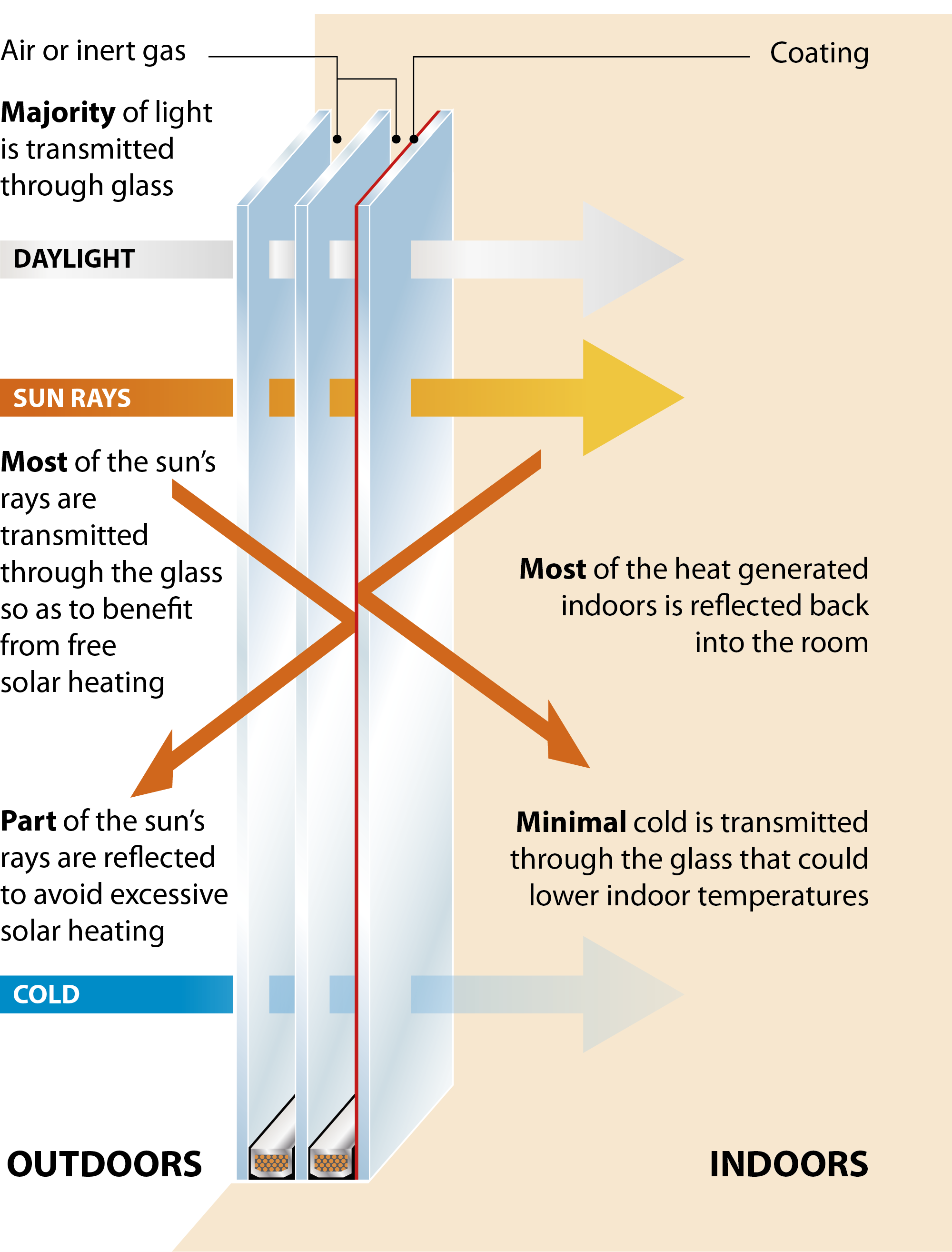
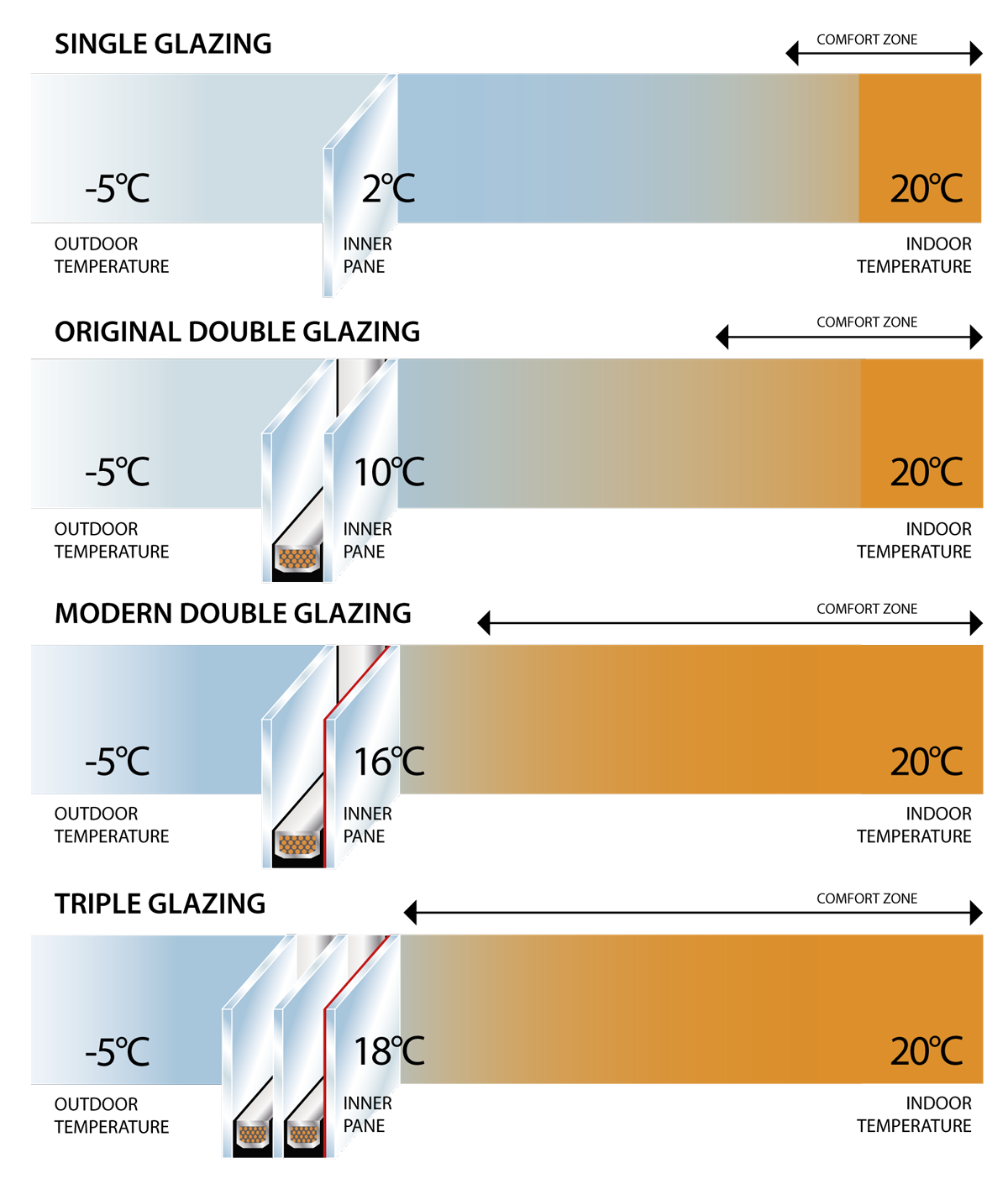
Single glazing allows much of the cold from outside to transmit into the house rapidly reducing the room temperature and necessitating the use of more heating. With a -5 degree outdoor temperature, the inner pane of the glass is only +2 degrees.
Pre-2000 double glazing without Low-E glass makes a significant improvement with inner panes now reaching +10 degrees, helping the room stay warmer.
Modern double glazing using Low-E glass makes an even greater improvement with inner pane temperature now up to +18 degrees. The Low-E coating reflects heat back into the room whilst reducing UV rays.
Triple glazing using Low-E glass means an inner pane temperature close to the ambient room temperature for maximum warmth and minimal heat loss.